This research focuses on a crucial project: a 1,000-ton all-304LN stainless steel structure. This project has a tight construction schedule and includes many high-precision machined parts. Therefore, we urgently need to improve processing efficiency and quality. Stainless steel cutting presents inherent difficulties. Also, we lack domestic application experience with 304LN stainless steel. Because of this, the project team believes we must study its processing characteristics in advance. This will guide subsequent large-scale production and help control costs.

We conducted rough milling, fine milling, drilling, and surface hardening processing experiments. We selected a variety of tools and different cutting parameters. Through these experiments, we studied the processing characteristics of 304LN stainless steel.
Rough Milling Test
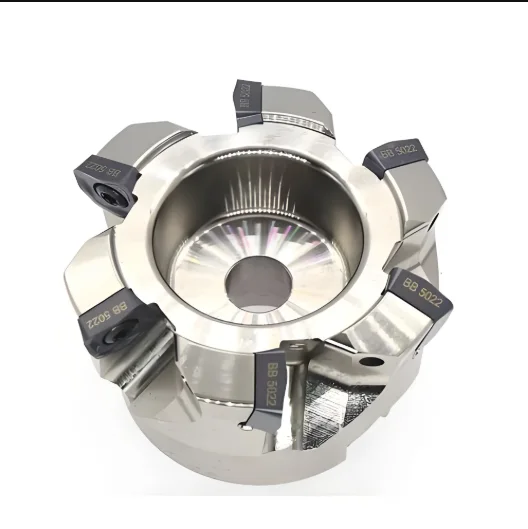
For the rough milling cutting tests, we used a JOMAX140 CNC milling and boring machining center. We tested two 160mm diameter fast feed face milling cutters: Kyocera (8 teeth) and Ceratizi (1 tooth). The test aimed to find and compare the best cutting parameters for both tools. We evaluated their cutting efficiency, service life, and cost. Figure 1 shows the setup.

The Kyocera cutter disc’s optimal cutting parameters are a cutting speed of 110 mm/min, a feed rate of 1.15 mm/Z, and a back cutting depth of 1 mm. The Ceratizi cutter disc’s optimal cutting parameters are a cutting speed of 140 min, a feed rate of 1 mm/Z, and a back cutting depth of 1.5 mm.
Let’s analyze the test results:
Service life
In dry milling, the Kyocera cutter head can continuously cut iron for 25 to 30 minutes. With coolant, it can continuously mill for nearly 60 minutes. The CERATIZ cutter head can continuously cut iron for 30 to 35 minutes in dry milling. With coolant, it can continuously mill for more than 60 minutes. The CERATIZ cutter head shows a slightly longer service life.
Cutting efficiency
The Kyocera cutter disc achieves a metal removal rate of 1.73×10 mm
3
/min. The Ceratizi cutter disc achieves 3.14×10 mm
3
/min. The Ceratizi cutter disc is more efficient than the Kyocera cutter disc.
Cost of use
A Kyocera blade costs 70 yuan per piece. A cutter disc with 8 blades costs 560 yuan. A Ceratisi blade costs 60 yuan per piece. A cutter disc with 1 blade costs 660 yuan. The Ceratisi cutter disc price is 18% higher. However, the Ceratisi cutter disc offers higher life and efficiency than Kyocera’s. After a comprehensive comparison, the Ceratisi cutter disc has a lower cost when processing the same number of parts.
Precision Milling Test
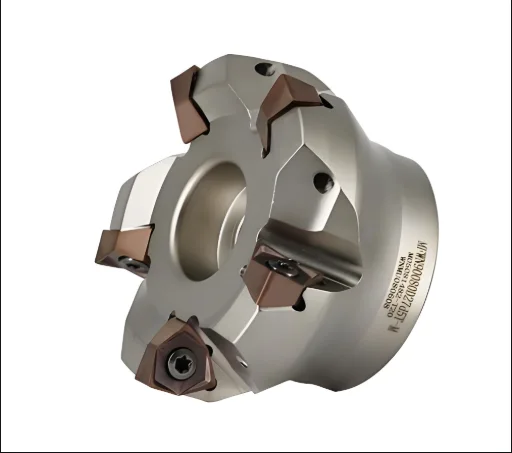
For the fine milling test, we selected two 90° cutters: Kyocera (100mm diameter, 7 teeth) and Sandvik (80mm diameter, 4 teeth). The test aimed to find the most suitable cutting parameters for these two tools through trial cutting. We then compared their cutting efficiency, service life, and cost. See Figure 2.

The optimal cutting parameters for both Kyocera and Sandvik cutters are a cutting speed of 100 mm/min, a feed rate of 0.38 mm/Z, and a back cutting depth of 1 mm. Figure 3 shows the test process. Let’s analyze the test results:

Service life
In dry milling, a single cutting edge of a Kyocera cutter can continuously mill for 30 minutes. With coolant, it can continuously mill for 50-60 minutes. A single cutting edge of a Sandvik cutter can continuously mill for 70 minutes in dry milling. With coolant, it can continuously mill for more than 120 minutes. The service life of a single cutting edge of a Sandvik cutter is more than twice that of a Kyocera cutter.
Cutting efficiency
The two cutters have the same cutting speeds. However, the Kyocera cutter’s single cutting edge has a shorter continuous cutting time. This means we change its cutting edge more frequently than the Sandvik cutters. Therefore, the Kyocera cutter has lower cutting efficiency than the Sandvik cutter.
Cost
A Kyocera cutter disc (7 pieces, total price 455 RMB) has 6 cutting edges per piece. It can dry mill for 180 minutes. A Sandvik cutter disc (4 pieces, total price 420 RMB) has 2 cutting edges per piece. It can dry mill for 140 minutes. Overall, the continuous processing cost of the Sandvik cutter disc is about 20% higher than that of Kyocera.
Comprehensive comparison
The Kyocera cutter disc has a lower service life and cutting efficiency than the Sandvik cutter disc. However, its cost of use is better than that of the Sandvik cutter disc. So, we can use both cutter discs in the fine milling process.
Drilling Test
We used two types of drills in the drilling test: twist drills and shallow hole drills. Although the stainless steel twist drill has a coating, its tip easily wears. The coating also falls off after grinding. This reduces durability and leads to low processing efficiency. In contrast, the shallow hole drill has an indexable design. We can directly replace the blade after wear, which is more convenient and efficient.
Surface Hardening Test
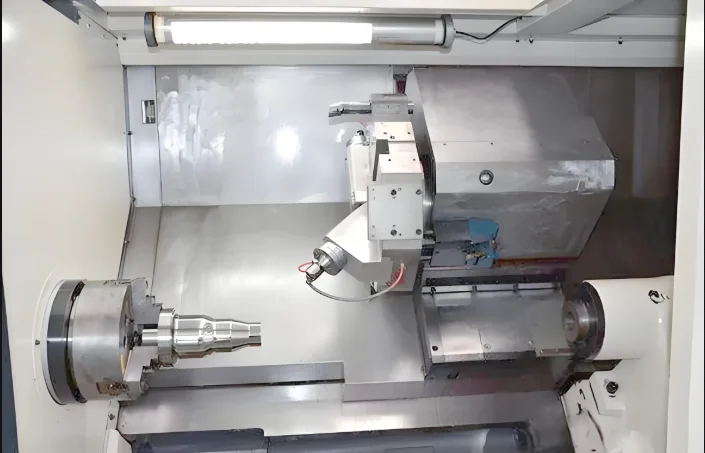
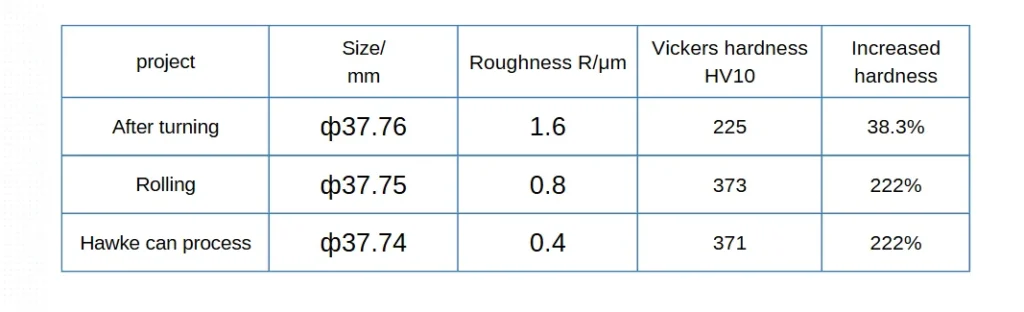
We performed the surface hardening test on a 304LN stainless steel bar using rolling and Hawking machining. The test process involved first turning the workpiece to the required depth. Then, we conducted the Hawking machining test. Finally, we tested the parts’ dimensional accuracy, roughness, and surface hardness.
Figure 4 shows the rolling and Hawking surface hardening test process. Figure 5 shows the surface hardening test piece.
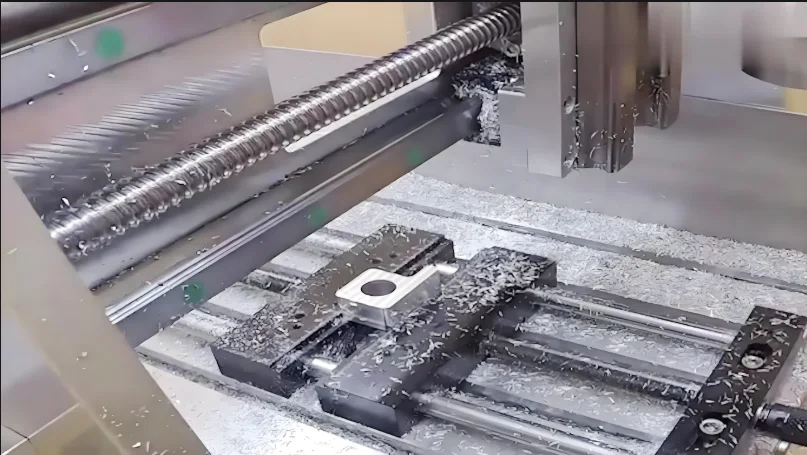


Table 1 presents the test data.
Conclusion
This stainless steel processing evaluation reached several conclusions. For rough milling, the Ceratizi cutterheads are superior to Kyocera in terms of life, efficiency, and cost. For fine milling, Kyocera and Sandvik cutterheads each have their advantages and disadvantages (cost versus life and efficiency). We can use both. When drilling, shallow hole drills are efficient, but cost and conditions limit them from completely replacing twist drills.
We need to use them in combination. Additionally, rolling and Hawking processing can significantly increase the hardness of the shallow surface layer of parts (HV10 371-373). They also reduce roughness (Ra within 0.8μm), and cause only small dimensional changes.
